Wireless Network Hacking
Wireless Basics
- 802.11 Series - defines the standards for wireless networks
- 802.15.1 - Bluetooth
- 802.15.4 - Zigbee - low power, low data rate, close proximity ad-hoc networks
- 802.16 - WiMAX - broadband wireless metropolitan area networks
| Wireless Standard | Operating Speed (Mbps) | Frequency (GHz) | Modulation Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 802.11a | 54 | 5 | OFDM |
| 802.11b | 11 | 2.4 | DSSS |
| 802.11d | Variation of a & b | Global use | |
| 802.11e | QoS Initiative | Data and voice | |
| 802.11g | 54 | 2.4 | OFDM and DSSS |
| 802.11i | WPA/WPA2 Encryption | ||
| 802.11n | 100+ | 2.4-5 | OFDM |
| 802.11ac | 1000 | 5 | QAM |
- Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) - carries waves in various channels
- Direct-Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) - combines all available waveforms into a single purpose
- Basic Service Set (BSS) - communication between a single AP and its clients
- Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID) - MAC address of the wireless access point
- Spectrum Analyzer - verifies wireless quality, detects rogue access points and detects attacks
- Directional antenna - signals in one direction; Yagi antenna is a type
- Omnidirectional antenna - signals in all directions
- Parapoblic grid antenna - based on principle of a satellite dish but it does not have a solid backing. They can pick up Wi-Fi singals ten miles or more
- Yagi antenna - unidirectional antenna used for 10MHz to VHF and UHF
- Dipole antenna - Bidrectional antenna used to support client connections rather than site to site applications
- Reflector antenna - Reflector antennas are used to concentrate EM energy which is radiated or recived at a focal point
- Service Set Identifier (SSID) - a text word (<= 32 char) that identifies network; provides no security
- Three Types of Authentication
- Open System - no authentication
- Shared Key Authentication - authentication through a shared key (password)
- Centralized Authentication - authentication through something like RADIUS
- Association is the act of connecting; authentication is the act of identifying the client
Wireless Encryption
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
- Doesn’t effectively encrypt anything
- Uses RC4 for encryption
- Original intent was to give wireless the same level of protection of an Ethernet hub
- Initialization Vector (IV) - used to calculate a 32 bit integrity check value (ICV)
- IVs are generally small and are frequently reused
- Sent in clear text as a part of the header
- This combined with RC4 makes it easy to decrypt the WEP key
- An attacker can send disassociate requests to the AP to generate a lot of these
- Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA or WPA2)
- WPA uses TKIP with a 128-bit key
- WPA changes the key every 10,000 packets
- WPA transfers keys back and forth during an Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
- WPA2 Enterprise - can tie an EAP or RADIUS server into the authentication
- WPA2 Personal - uses a pre-shared key to authenticate
- WPA2 uses AES for encryption
- WPA2 ensures FIPS 140-2 compliance
- WPA2 uses CCMP instead of TKIP
- Message Integrity Codes (MIC) - hashes for CCMP to protect integrity
- Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code (CBC-MAC) - integrity process of WPA2
| Wireless Standard | Encryption | IV Size (Bits) | Key Length (Bits) | Integrity Check |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WEP | RC4 | 24 | 40/104 | CRC-32 |
| WPA | RC4 + TKIP | 48 | 128 | Michael/CRC-32 |
| WPA2 | AES-CCMP | 48 | 128 | CBC-MAC (CCMP) |
Wireless Hacking
- Threats
- Access Control Attacks - Evading WLAN access control messures such as AP MAC filtering and Wi-Fi port accss
-
Integrity Attacks - Send forged control, managment or data frames over a wireless network to misdirect the wirless device
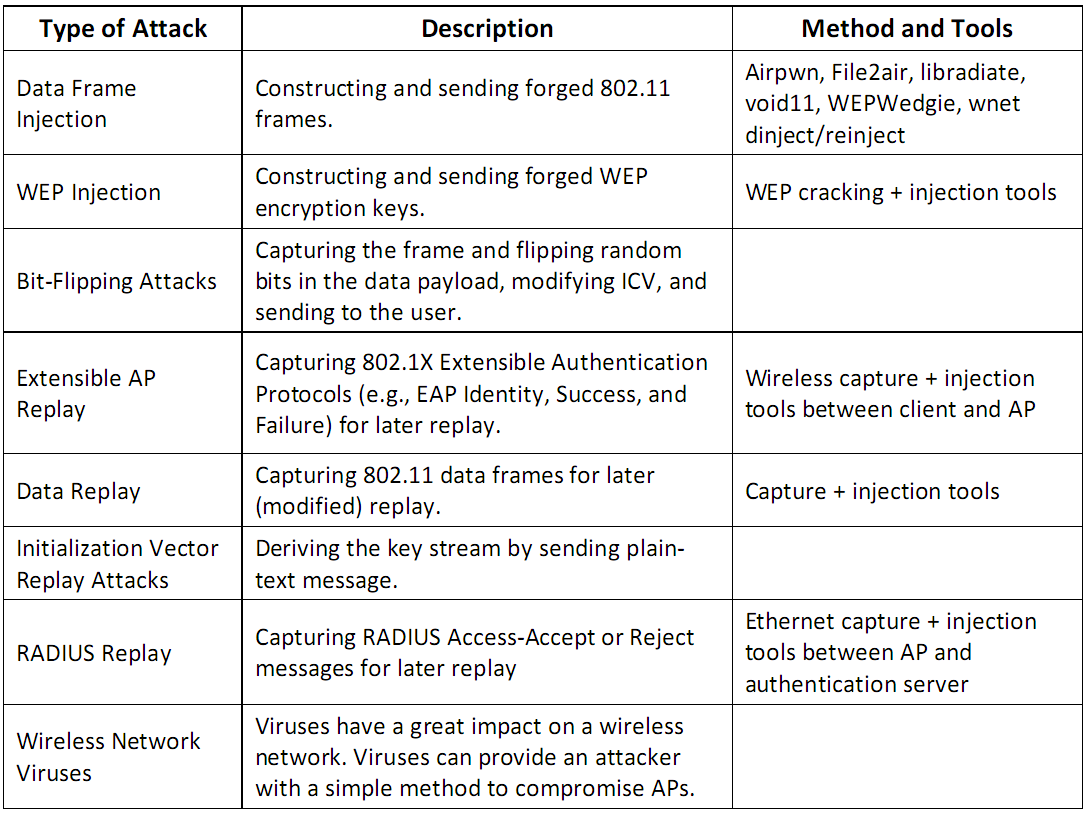
- Confidentiality Attacks - Intercept confidential information send over wireless associations
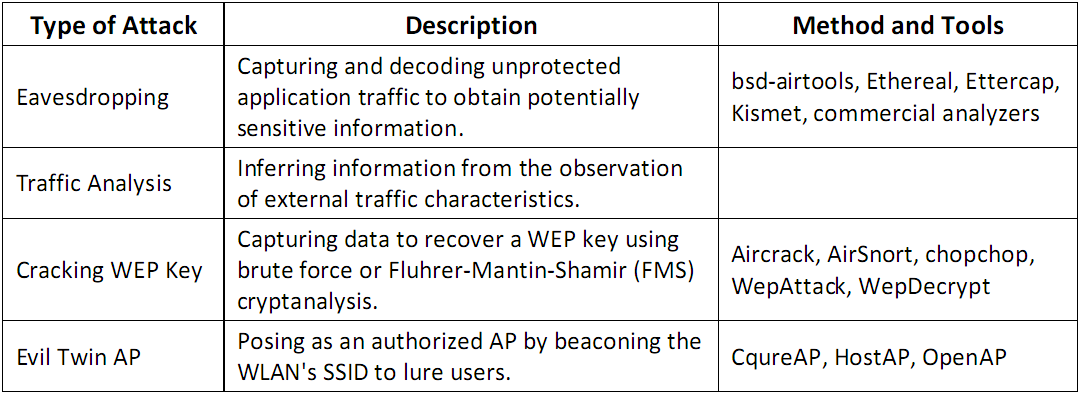
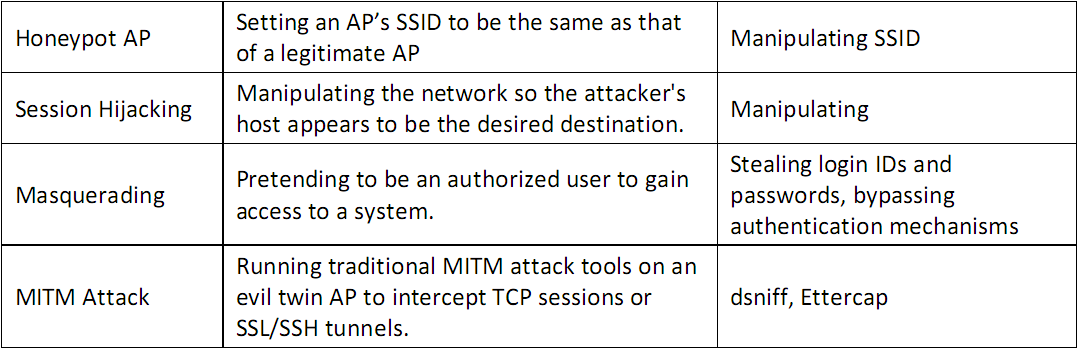
- Availability Attacks - obstructing the delivery of wirelesss serrvices to legitmate users
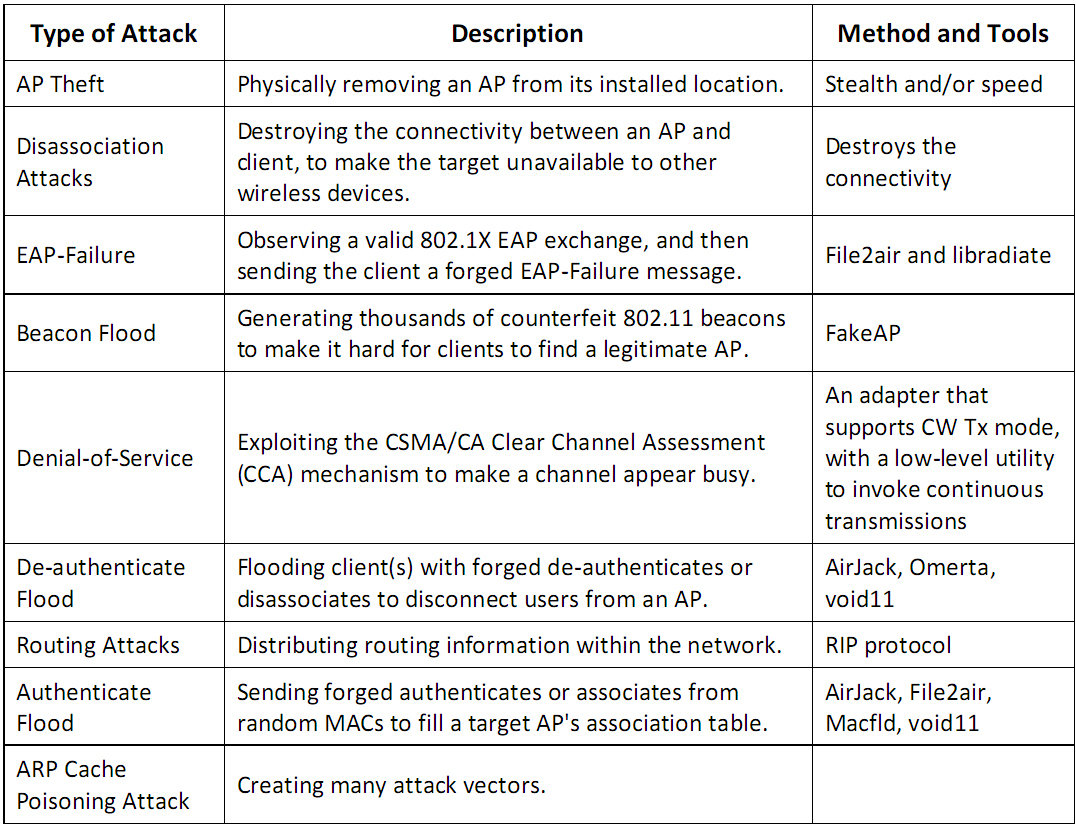
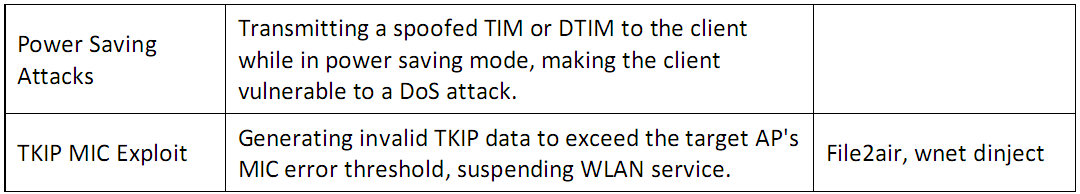
- Authentication Attacks - steal the identity of Wi-Fi clients
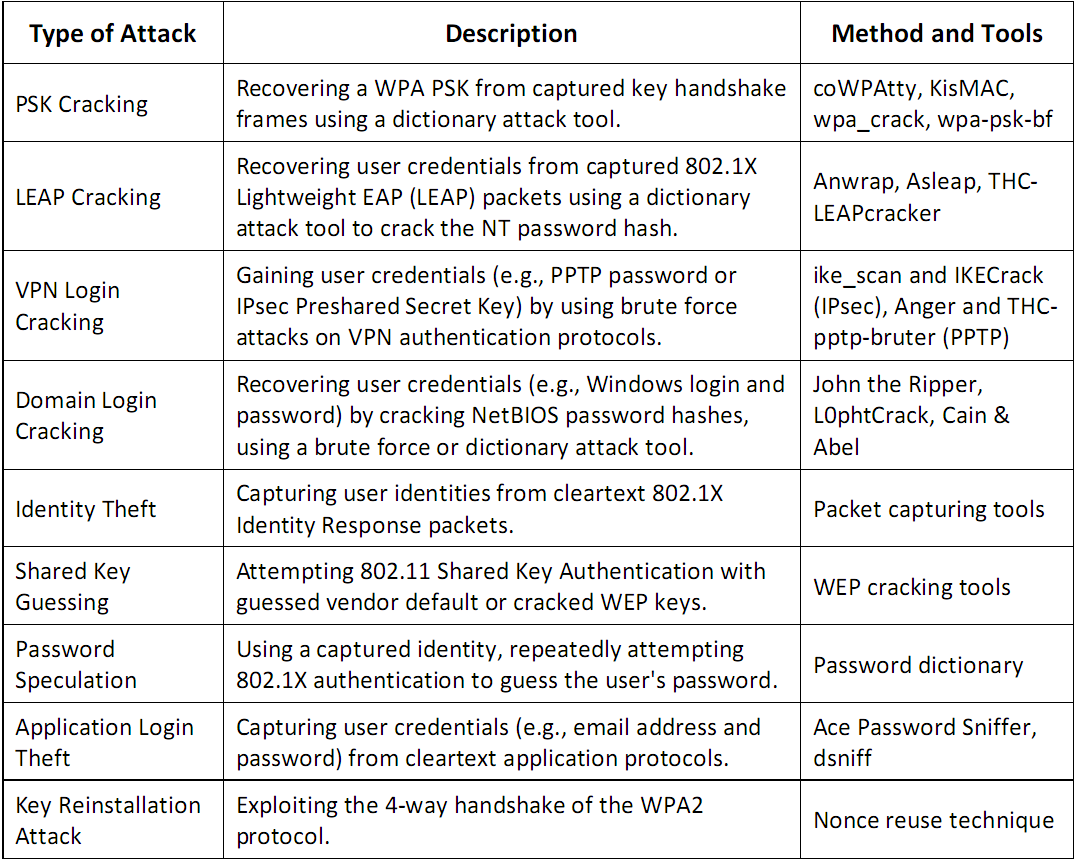
- Network Discovery
- Wardriving, warflying, warwalking, etc.
- Tools such as WiFiExplorer, WiFiFoFum, OpenSignalMaps, WiFinder
- WIGLE - map for wireless networks
- NetStumbler - tool to find networks
- Kismet - wireless packet analyzer/sniffer that can be used for discovery
- Works without sending any packets (passively)
- Can detects access points that have not been configured
- Works by channel hopping
- Can discover networks not sending beacon frames
- Ability to sniff packets and save them to a log file (readable by Wireshark/tcpdump)
- NetSurveyor - tool for Windows that does similar features to NetStumbler and Kismet
- Doesn’t require special drivers
- WiFi Adapter
- AirPcap is mentioned for Windows, but isn’t made anymore
- pcap - driver library for Windows
- libpcap - drivery library for Linux
Wireless Attacks
- Rogue Access Point - places an access point controlled by an attacker
- Evil Twin - a rogue AP with a SSID similar to the name of a popular network
- Also known as a mis-association attack
- Honeyspot - faking a well-known hotspot with a rogue AP
- Ad Hoc Connection Attack - connecting directly to another phone via ad-hoc network
- Not very successful as the other user has to accept connection
- DoS Attack - either sends de-auth packets to the AP or jam the wireless signal
- With a de-auth, you can have the users conect to your AP instead if it has the same name
- Jammers are very dangerous as they are illegal
- MAC Filter - only allows certain MAC addresses on a network
- Easily broken because you can sniff out MAC addresses already connected and spoof it
- Tools for spoofing include SMAC and TMAC
Wireless Encryption Attacks
- WEP Cracking
- Easy to do because of weak IVs
- Process
- Start a compatible adapter with injection and sniffing capabilities
- Start a sniffer to capture packets
- Force the creation of thousands of packets (generally with de-auth)
- Analyze captured packets
- Tools
- Aircrack-ng - sniffer, detector, traffic analysis tool and a password cracker
- Uses dictionary attacks for WPA and WPA 2. Other attacks are for WEP only

- Uses dictionary attacks for WPA and WPA 2. Other attacks are for WEP only
- Cain and Abel - sniffs packets and cracks passwords (may take longer)
- Relies on statistical measures and the PTW technique to break WEP
- KisMAC - MacOS tool to brute force WEP or WPA passwords
- WEPAttack
- WEPCrack
- Portable Penetrator
- Elcomsoft’s Wireless Security Auditor
- Aircrack-ng - sniffer, detector, traffic analysis tool and a password cracker
- Methods to crack include PTW, FMS, and Korek technique
- WPA Cracking
- Much more difficult than WEP
- Uses a constantly changing temporal key and user-defined password
- Key Reinstallation Attack (KRACK) - replay attack that uses third handshake of another device’s session
- Works by exploiting the 4-way handshake of the WPA2 protocol by forciing Nonce reuse
- Works against all modern protected Wi-Fi Networks
- Most other attacks are simply brute-forcing the password
Wireless Sniffing
- Very similar to sniffing a wired network
- Tools
- NetStumbler
- Kismet
- OmniPeek - provides data like Wireshark in addition to network activity and monitoring
- AirMagnet WiFi Analyzer Pro - sniffer, traffic analyzer and network-auditing suite
- WiFi Pilot
Bluetooth Hacking
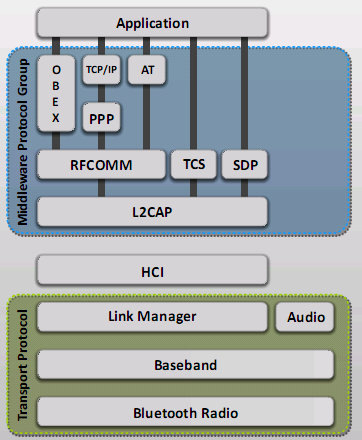
- Bluetooth Stack - replaces the cables connection portable or fixed devices
- Attacks
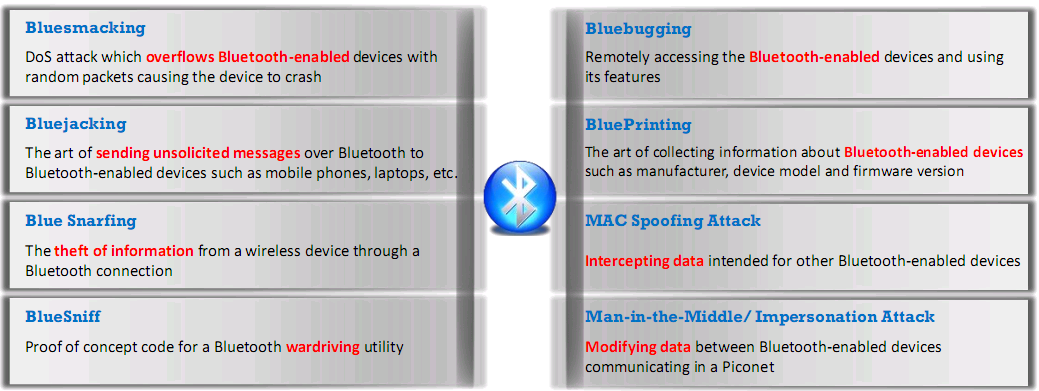
- Threats

- Tools
- Bluetooth View